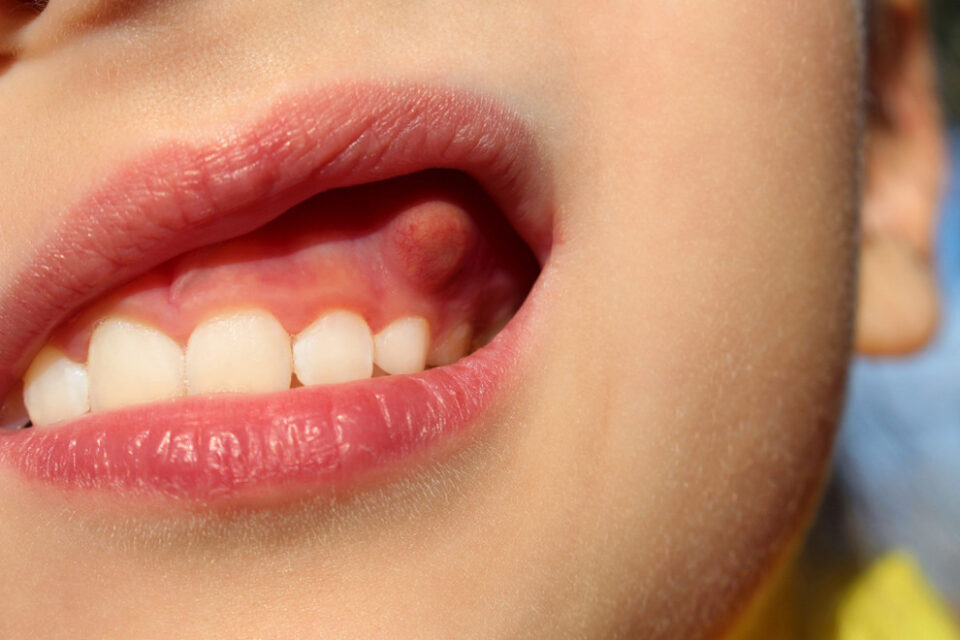
Bumps or lumps on the gums can be a cause for concern for many people. While they can be benign, they may also indicate an underlying dental issue that requires attention. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments can empower individuals to seek the right help and maintain good oral health.
Causes of Bumps on Gums
Bumps on the gums can arise due to various factors, including:
-
- Gingival Hyperplasia: This condition involves the overgrowth of gum tissue, often resulting from poor oral hygiene, hormonal changes, certain medications (like anticonvulsants), or systemic conditions.
- Gingival Hyperplasia: This condition involves the overgrowth of gum tissue, often resulting from poor oral hygiene, hormonal changes, certain medications (like anticonvulsants), or systemic conditions.
-
- Cysts: Dental cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop on the gums. They can be associated with tooth roots or occur independently and often arise due to infection or inflammation.
- Cysts: Dental cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop on the gums. They can be associated with tooth roots or occur independently and often arise due to infection or inflammation.
-
- Abscesses: An abscess is a localized collection of pus caused by bacterial infection. This can occur in the gums or around the root of a tooth and may result from untreated dental decay or periodontal disease.
- Abscesses: An abscess is a localized collection of pus caused by bacterial infection. This can occur in the gums or around the root of a tooth and may result from untreated dental decay or periodontal disease.
-
- Mucoceles: These are benign, fluid-filled swellings that typically occur on the minor salivary glands in the mouth. They can appear as painless bumps and may resolve on their own or require medical intervention.
- Mucoceles: These are benign, fluid-filled swellings that typically occur on the minor salivary glands in the mouth. They can appear as painless bumps and may resolve on their own or require medical intervention.
-
- Oral Fibromas: These are benign tumors that can develop in the oral cavity, including the gums. They often arise due to irritation or injury and usually do not require treatment unless they cause discomfort or cosmetic concerns.
- Oral Fibromas: These are benign tumors that can develop in the oral cavity, including the gums. They often arise due to irritation or injury and usually do not require treatment unless they cause discomfort or cosmetic concerns.
-
- Periodontal Disease: Gum disease, particularly in its advanced stages, can lead to bumps and lumps caused by inflammation, infection, or pockets of pus forming in the gums.
- Periodontal Disease: Gum disease, particularly in its advanced stages, can lead to bumps and lumps caused by inflammation, infection, or pockets of pus forming in the gums.
-
- Allergic Reactions: Allergies to dental materials, toothpaste, or certain foods can cause localized swelling, leading to the formation of bumps on the gums.
- Allergic Reactions: Allergies to dental materials, toothpaste, or certain foods can cause localized swelling, leading to the formation of bumps on the gums.
-
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can lead to gum sensitivity and swelling, sometimes manifesting as small bumps.
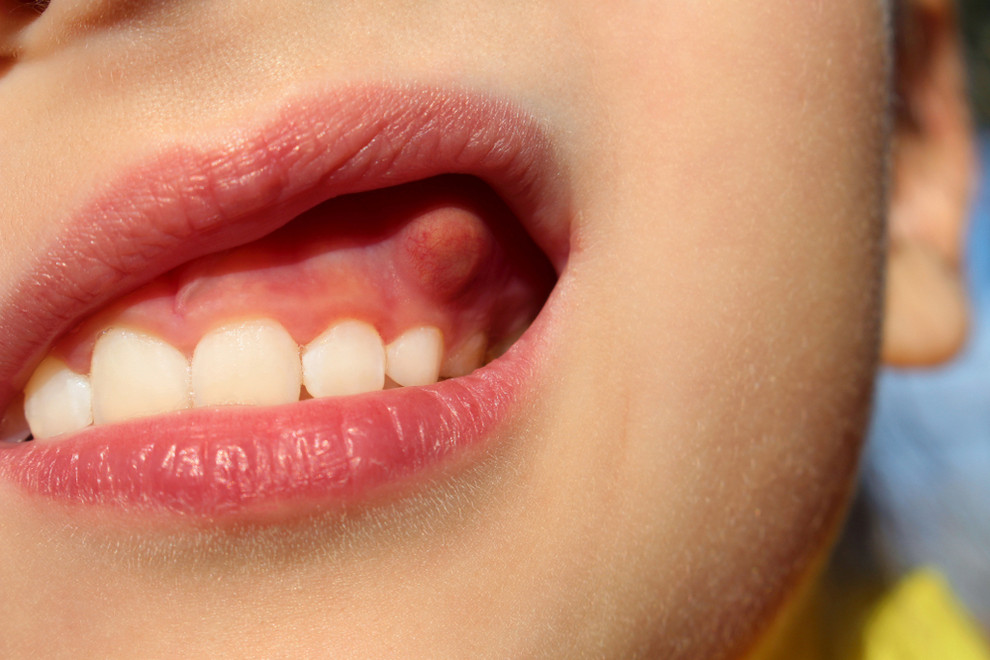

Symptoms Associated with Bumps on Gums
The presence of bumps on the gums may accompany other symptoms, which can help in identifying the underlying issue:
-
- Pain or Discomfort: Some bumps may be painless, while others can lead to significant discomfort, especially if there is an underlying infection.
- Pain or Discomfort: Some bumps may be painless, while others can lead to significant discomfort, especially if there is an underlying infection.
-
- Bleeding: Inflamed or infected gums may bleed, particularly when brushing or flossing.
- Bleeding: Inflamed or infected gums may bleed, particularly when brushing or flossing.
-
- Swelling: Surrounding gum tissue may also become swollen, red, or tender.
- Swelling: Surrounding gum tissue may also become swollen, red, or tender.
-
- Bad Breath: Foul-smelling breath (halitosis) can indicate an infection, abscess, or periodontal disease.
- Bad Breath: Foul-smelling breath (halitosis) can indicate an infection, abscess, or periodontal disease.
-
- Fever or Malaise: In cases of severe infection, systemic symptoms such as fever or a general feeling of being unwell may occur.
- Fever or Malaise: In cases of severe infection, systemic symptoms such as fever or a general feeling of being unwell may occur.
-
- Oral Lesions: Development of sores or ulcers in addition to the bumps could indicate a viral or autoimmune issue, like oral herpes or lichen planus.
When to See a Dentist
It is crucial to consult a dentist if you notice any of the following:
-
- The bump lasts longer than two weeks.
-
- There’s persistent pain associated with the bump.
-
- You experience swelling that spreads beyond the gum area.
-
- You notice changes in your bite or have difficulty chewing.
-
- There’s an accompanying fever or systemic ill-feeling.
Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing potential complications, including tooth loss or severe infections.
Treatment Options
The treatment for bumps on the gums will depend on the underlying cause:
-
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Improved dental care, including regular brushing and flossing, and routine dental cleanings can help manage gum issues.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Improved dental care, including regular brushing and flossing, and routine dental cleanings can help manage gum issues.
-
- Medications: Antibiotics may be prescribed for infections, while corticosteroids can reduce inflammation.
- Medications: Antibiotics may be prescribed for infections, while corticosteroids can reduce inflammation.
-
- Surgical Intervention: In cases like cysts or abscesses, drainage procedures or surgical removal may be necessary.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases like cysts or abscesses, drainage procedures or surgical removal may be necessary.
-
- Dental Work: Addressing underlying oral health issues, such as periodontal disease, may involve deep cleaning (scaling and root planing) or more invasive treatments like bone grafts or gum surgery.
- Dental Work: Addressing underlying oral health issues, such as periodontal disease, may involve deep cleaning (scaling and root planing) or more invasive treatments like bone grafts or gum surgery.
-
- Monitoring: Some benign bumps, like fibromas or mucoceles, may just need regular monitoring if they aren’t causing issues.
Conclusion
Bumps on the gums can vary widely in cause and significance, from harmless irritation to more serious dental conditions. Understanding the potential causes and symptoms can help individuals take proactive steps in seeking care and maintaining their oral health. Regular dental visits, good oral hygiene practices, and paying attention to changes in your oral cavity can go a long way in preventing more serious complications down the line. If uncertain, don’t hesitate to reach out to a dental professional for advice and treatment options tailored to your specific needs.